What’s A Good Cpu Temperature – Tips for Monitoring!
Discover what’s a good CPU temperature for optimal performance and longevity. Learn tips to monitor, maintain, and manage your CPU temperatures effectively.
In this article, we explain what constitutes a good CPU temperature for both idle and high-performance tasks. You’ll learn how to monitor CPU temperatures, identify overheating signs, and maintain optimal cooling. Plus, we share practical tips to ensure your system runs efficiently and stays protected from heat damage.
What’s a Good CPU Temperature?

Your CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the heart of your computer, and keeping it at the right temperature is essential for performance and longevity. Whether you’re gaming, working on intensive tasks, or just browsing the web, understanding what’s a good CPU temperature can prevent overheating and ensure your system runs smoothly. In this guide, we’ll explore what constitutes a healthy CPU temperature, factors affecting it, and how to monitor and manage it effectively.
Understanding CPU Temperature Ranges:
A good CPU temperature varies depending on the workload and your CPU model. However, there are general benchmarks you can follow:
Idle Temperatures:
When your computer is idle or performing basic tasks like browsing, a CPU temperature between 30°C and 50°C (86°F to 122°F) is considered normal.
Under Load Temperatures:
During intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or rendering, your CPU temperature can rise. A safe range under load is typically 60°C to 80°C (140°F to 176°F). Some high-performance CPUs may tolerate temperatures slightly above this range.
Maximum Temperatures:
Most CPUs have a maximum safe operating temperature, often referred to as the TjMax (junction temperature maximum). This is usually between 90°C and 100°C (194°F to 212°F). Consistently reaching or exceeding this limit can lead to thermal throttling, reduced performance, and potential hardware damage.
Read More:What Games Are Cpu Intensive – A Comprehensive Guide!
Factors That Influence CPU Temperature:
1. Workload Intensity:
Heavy tasks like gaming, streaming, and 3D rendering push your CPU harder, generating more heat. Conversely, light tasks require less power and produce less heat.
2. Ambient Room Temperature:
The temperature of your surroundings plays a significant role. If you’re in a hot environment, your CPU’s cooling system will work harder to maintain optimal temperatures.
3. Cooling Solutions:
- Air Cooling: Standard air coolers are effective for most users, but their efficiency depends on airflow and the quality of the heatsink.
- Liquid Cooling: Liquid coolers are more efficient at dissipating heat, especially for overclocked systems or high-performance CPUs.
4. Thermal Paste:
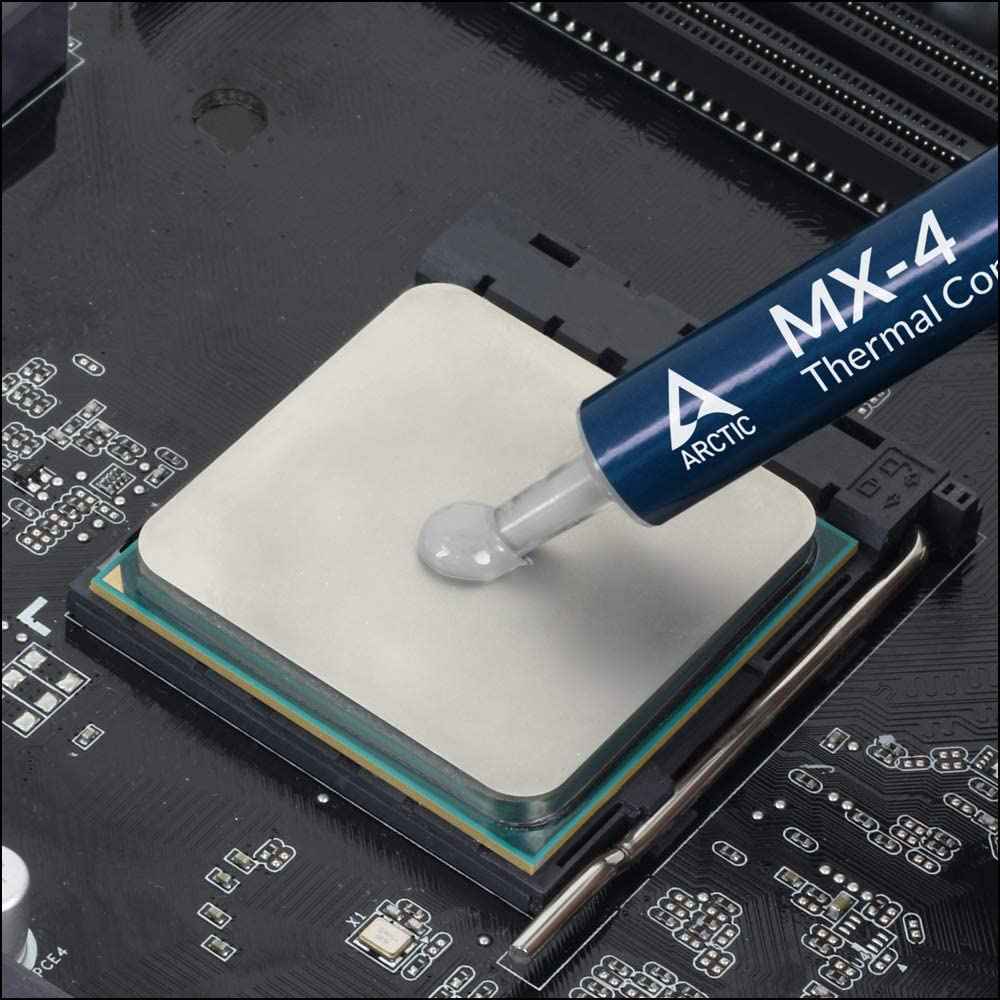

The thermal paste between your CPU and cooler ensures efficient heat transfer. Over time, thermal paste can degrade, leading to higher temperatures.
5. Dust and Dirt:
Dust accumulation in your computer’s fans and vents can block airflow, causing the CPU to overheat.
6. Overclocking:
Increasing your CPU’s clock speed boosts performance but also increases heat output. Overclocking requires enhanced cooling solutions to maintain safe temperatures.
How to Monitor CPU Temperature?
1. BIOS/UEFI:
Most motherboards allow you to check your CPU temperature directly through the BIOS or UEFI. Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI by pressing a key like Del, F2, or Esc during boot-up.
2. Software Tools:
Various software applications provide real-time CPU temperature monitoring:
- HWMonitor
- Core Temp
- MSI Afterburner
- Open Hardware Monitor
These tools display CPU temperature along with other hardware stats like voltage and fan speeds.
3. Built-in Monitoring Utilities:
Many modern CPUs come with built-in monitoring features accessible through their software suites, such as AMD Ryzen Master or Intel Extreme Tuning Utility.
Read More:Is 60 Celsius Hot For Cpu – A Comprehensive Guide!
Tips to Maintain Optimal CPU Temperature:
1. Improve Airflow:
Ensure your computer case has good airflow by adding additional fans if necessary. Place your PC in a well-ventilated area, away from walls or heat sources.
2. Upgrade Cooling Systems:
Consider upgrading your cooling system if you frequently experience high temperatures. Options include better air coolers or liquid cooling solutions.
3. Clean Your PC Regularly:
Dust buildup can significantly impact cooling efficiency. Use compressed air to clean your fans, heatsinks, and vents every few months.
4. Apply New Thermal Paste:
If your CPU temperatures are rising despite clean components and good airflow, reapply thermal paste. Be sure to use high-quality thermal paste and follow proper application techniques.
5. Avoid Overclocking:
If cooling is insufficient, avoid overclocking your CPU. Instead, stick to the manufacturer’s recommended settings.
6. Monitor Ambient Temperature:

If you’re in a hot climate, consider using air conditioning or placing your computer in a cooler area to help reduce CPU temperature.
7. Enable Power Saving Modes:
Modern CPUs have power-saving features that reduce heat generation during low-demand tasks. Enable these settings in your operating system or BIOS.
Signs of Overheating:
An overheating CPU can cause several issues, including:
- System Crashes: Unexpected shutdowns or restarts.
- Thermal Throttling: Reduced performance as the CPU lowers its speed to prevent damage.
- Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): Critical errors often related to hardware instability.
- Excessive Fan Noise: Your cooling system working overtime to dissipate heat.
Is Your CPU Running Hot? Here’s What to Do!
- Check Cooling: Ensure all fans are working correctly and that your heatsink is securely attached.
- Reapply Thermal Paste: Replace old thermal paste to improve heat transfer.
- Upgrade Cooling: Consider a high-performance cooler if your current one is insufficient.
- Check for Malware: Malware can cause your CPU to run at high loads unnecessarily.
- Limit Background Processes: Use Task Manager to close unnecessary programs.
FAQ’s
1. What is a normal idle CPU temperature?
A normal idle CPU temperature ranges between 30°C and 50°C.
2. What is a safe CPU temperature under load?
Under load, a safe CPU temperature is typically 60°C to 80°C, depending on the CPU model.
3. What happens if my CPU temperature gets too high?
High CPU temperatures can cause thermal throttling, system instability, or permanent hardware damage.
4. How can I check my CPU temperature?
You can check your CPU temperature using software tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or through your BIOS/UEFI.
5. How do I lower my CPU temperature?
Improve airflow, clean your PC regularly, upgrade your cooling system, or reapply thermal paste to lower CPU temperatures.
Conclusion:
Understanding what’s a good CPU temperature is crucial for maintaining your computer’s health and performance. By keeping idle temperatures between 30°C and 50°C, and load temperatures below 80°C, you can avoid overheating and prolong the lifespan of your CPU.
Regular maintenance, proper cooling, and temperature monitoring are key to ensuring your system remains stable and efficient.