The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu – Key Insights!
Discover how the CPU, the brain of the computer, powers processes and data. Explore why The Brain Of The Computer Is The CPU and essential for performance!
In this article, we explore why The Brain Of The Computer Is The CPU and its vital role in powering your system. Learn how the CPU handles processes, calculations, and data management for seamless performance. Gain insights into its key components and their impact on computing efficiency.
What Is the CPU?

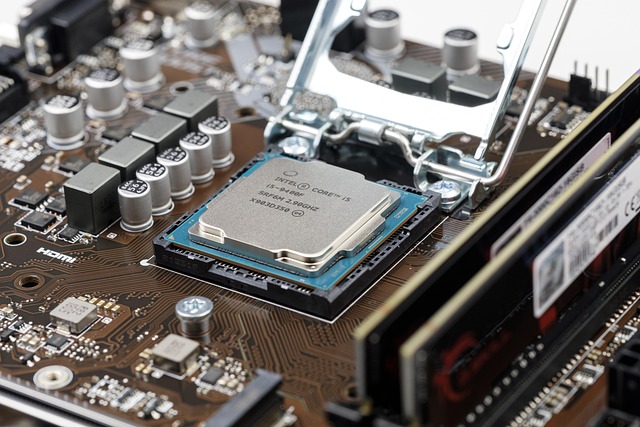
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is a small, powerful chip embedded in your computer’s motherboard. It executes instructions from software applications and processes data to perform tasks. The CPU handles everything from opening a web browser to running video games or compiling code.
The CPU is an essential component in computers, smartphones, tablets, and even modern appliances like smart TVs and refrigerators. Its performance significantly impacts how fast and efficiently a device operates.
Why Is the CPU Called the Brain of the Computer?
Just as the brain processes information and directs actions in the human body, the CPU performs a similar role in a computer. Here are the parallels that explain this analogy:
- Decision Making: The CPU makes critical decisions by interpreting and executing program instructions. It determines what action to perform and in what sequence.
- Data Processing: The CPU processes input data received from peripherals like keyboards, mice, or sensors and converts it into meaningful outputs, such as displaying text on a screen.
- Coordination: Like the brain coordinates different body parts, the CPU synchronizes the activities of other computer components, such as memory, storage, and the graphics card.
How Does the CPU Work? The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu!
The CPU’s functionality revolves around its ability to fetch, decode, and execute instructions—a process commonly known as the instruction cycle.
- Fetch: The CPU retrieves instructions from the computer’s memory.
- Decode: It translates the fetched instructions into a format it can understand.
- Execute: The CPU performs the specified operation, such as arithmetic calculations, logical comparisons, or data transfer.
- Store: Finally, the results of the operation are written back to memory or sent to an output device.
Read More:Psu Cpu Cable Doesn’t Match – A Complete Guide!
Key Components of the CPU:
The CPU comprises several integral parts, each playing a specific role in its operation:
- Control Unit (CU): The CU directs the flow of data between the CPU and other components. It ensures that instructions are executed in the correct sequence.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, AND, OR, and comparisons.
- Registers: These are small, high-speed storage locations within the CPU that hold data temporarily during processing.
- Cache Memory: The CPU cache stores frequently accessed data and instructions to reduce latency and enhance processing speed.
- Clock: The CPU’s clock governs its speed, dictating how many operations it can perform per second, measured in gigahertz (GHz).
Types of CPUs: The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu!
CPUs come in various types and configurations to cater to different computing needs:
- Desktop CPUs: Designed for personal computers, these CPUs are versatile and offer robust performance for general computing tasks, gaming, and professional applications.
- Laptop CPUs: Optimized for energy efficiency and heat management, laptop CPUs provide adequate performance without draining battery life.
- Server CPUs: Built for reliability and scalability, server CPUs handle demanding workloads, such as database management and web hosting.
- Mobile CPUs: Found in smartphones and tablets, these CPUs focus on low power consumption while delivering excellent performance for mobile apps.
- Embedded CPUs: Used in specialized devices like ATMs and automotive systems, these CPUs are designed for specific tasks and environments.
Factors That Influence CPU Performance:
Several factors determine how well a CPU performs:
- Core Count: Modern CPUs have multiple cores, enabling them to execute multiple tasks simultaneously. More cores generally mean better multitasking and performance in multi-threaded applications.
- Clock Speed: Measured in GHz, the clock speed indicates how many instructions a CPU can execute per second. Higher clock speeds translate to faster processing.
- Cache Size: Larger cache sizes allow the CPU to access data more quickly, reducing the need to fetch it from slower main memory.
- Architecture: The CPU’s design and manufacturing process influence its efficiency and performance. Newer architectures are typically faster and more power-efficient.
- Thermal Management: Effective cooling solutions are essential to prevent overheating and maintain optimal CPU performance.
Future Trends in CPU Technology:
As technology advances, CPUs continue to evolve, offering greater performance and efficiency. Here are some emerging trends:
- Smaller Transistors: Advances in semiconductor technology are enabling the production of smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient transistors.
- Increased Core Counts: CPUs are incorporating more cores to handle parallel processing tasks effectively.
- AI Integration: Modern CPUs are being designed with dedicated hardware for artificial intelligence and machine learning applications.
- Energy Efficiency: CPUs are becoming more power-efficient, extending battery life in portable devices and reducing energy consumption in data centers.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its infancy, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize processing power, solving complex problems far beyond the reach of traditional CPUs.
Read More:Microcenter 25 Off Cpu – Tips and Tricks!
Why the CPU Matters to Everyday Users?
For the average user, the CPU’s performance determines how quickly their computer can complete tasks. A powerful CPU ensures:
- Smooth multitasking: Switching between applications is seamless.
- Faster processing: Tasks like photo editing, video rendering, and gaming run efficiently.
- Better user experience: Quick responses and minimal lag enhance overall satisfaction.
FAQ’s The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu!
1. What does the CPU do in a computer?
The CPU processes instructions, performs calculations, and manages data transfer between components.
2. What makes the CPU the most critical component of a computer?
The CPU is critical because it executes instructions, processes data, and coordinates all computer components for smooth operation.
3. What are the key components of a CPU?
The main components are the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit (CU), and registers.
4. Does the CPU affect a computer’s speed?
The CPU’s clock speed and core count determine how quickly it processes data, directly affecting overall system performance and efficiency.
5. Can a computer function without a CPU?
The CPU is essential for executing instructions, running programs, performing calculations, managing data flow, and coordinating computer operations efficiently.
Conclusion: The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu!
The CPU is aptly called the brain of the computer because of its vital role in processing instructions, making decisions, and coordinating all operations. As technology continues to advance, the CPU remains a cornerstone of computing, driving innovation and enabling us to achieve more in less time. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech enthusiast, understanding the CPU’s significance can help you make informed decisions when choosing a device or optimizing its performance.