How Much Power Does My Cpu Use – A Complete Guide!
Learn how much power your CPU uses, how to measure it, and ways to optimize energy for better performance in your system.
In this article, we explore how much power your CPU uses, factors affecting power consumption, and typical usage for popular processors. Learn how to measure and optimize CPU energy usage. Discover practical tips to enhance performance, reduce energy costs, and improve hardware longevity.
What Determines CPU Power Usage?
CPU power usage, often referred to as Thermal Design Power (TDP), is the maximum amount of heat a processor generates under heavy workloads. This measurement is usually expressed in watts. However, actual power usage can vary depending on several factors:
Processor Type:
- High-performance CPUs (e.g., Intel Core i9, AMD Ryzen 9) consume more power due to their higher core count and clock speeds.
- Energy-efficient processors (e.g., Intel Core i3, AMD Ryzen 5) are designed for low power consumption, making them ideal for laptops or low-power desktops.
Clock Speed and Voltage:
- Higher clock speeds increase power consumption as the CPU works harder to execute tasks.
- Voltage scaling also impacts power usage; higher voltages result in greater energy draw.
Workload Intensity:
- Power usage spikes during intensive tasks such as gaming, video rendering, or scientific simulations.
- Light tasks like web browsing or word processing use significantly less power.
Overclocking:
- Overclocking increases clock speed and voltage, leading to higher power usage and heat output.
Read More:The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu – Key Insights!
Manufacturing Process:
- Modern CPUs are built using smaller nanometer (nm) processes, which improve efficiency. For example, a 7nm CPU consumes less power compared to a 14nm processor while delivering similar or better performance.
Typical Power Consumption of Popular CPUs:
Here’s a general estimate of power consumption for some popular CPU models:
| Cpu Model | TDP (watts) | Typical power usage |
| Intel core i3-12100k | 60w | 25w-50w |
| Intel core i9-13900k | 125w | 60w-250w |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600 | 65w | 40w-90w |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950x | 170w | 80w-200w |
| Apple M2 (ARM) | 20w | 5w-25w |
Note: These numbers are approximate and vary depending on system configuration and workload.
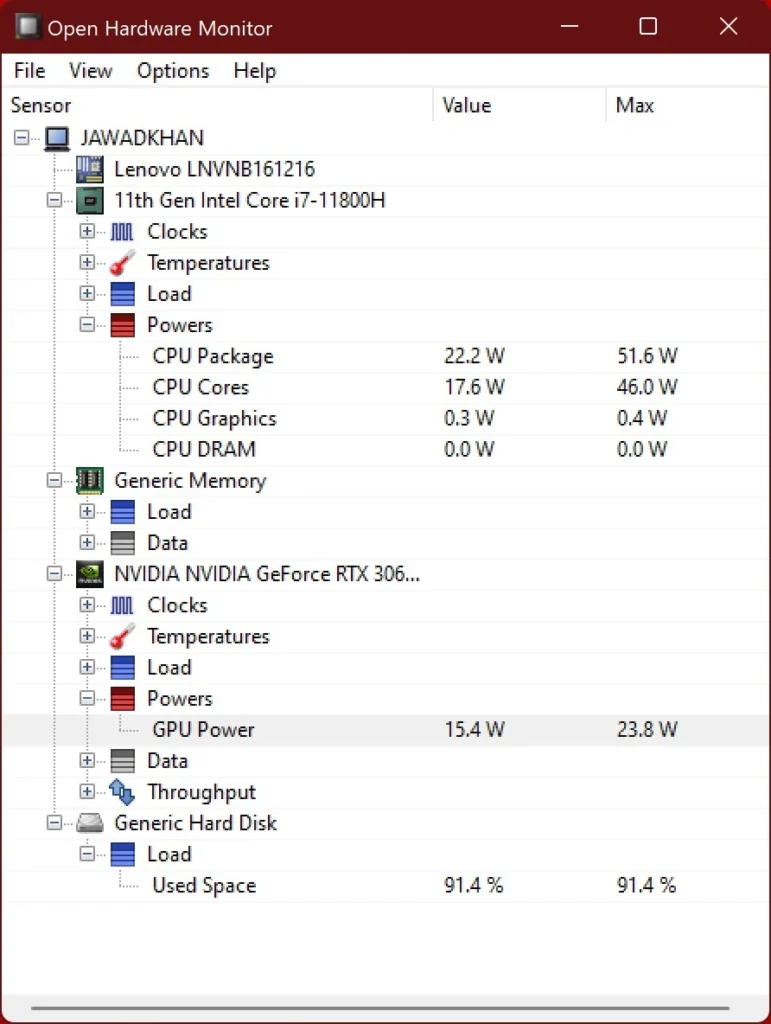
How to Measure CPU Power Usage?
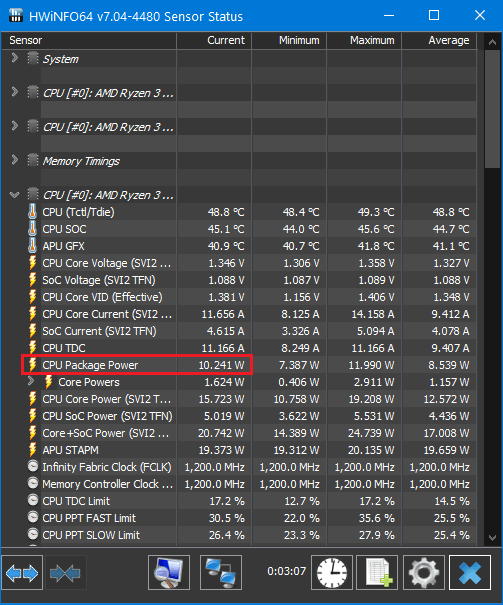
Measuring your CPU’s power usage can provide real-time insights into its energy consumption. Here are some methods to do this:
Built-In Monitoring Tools:
- Many modern motherboards come with BIOS/UEFI features that display CPU power consumption.
Software Tools:
- HWMonitor: Displays detailed information about power usage, temperatures, and voltages.
- Core Temp: Focuses on CPU temperature and power draw.
- Intel Power Gadget: Specific to Intel CPUs, providing real-time power and thermal readings.
External Power Meters:
- Plug your computer into a wall power meter to measure the entire system’s power consumption. Subtract the power used by other components (GPU, PSU inefficiencies, etc.) to estimate the CPU’s draw.
Task Manager (Windows):
- On Windows, you can check CPU usage percentage to estimate energy consumption indirectly. However, it’s not as precise as dedicated tools.
How to Optimize CPU Power Usage?
Optimizing CPU power usage can lower electricity bills, extend hardware lifespan, and reduce heat output. Here are some strategies:
Enable Power-Saving Modes:
- Use your operating system’s power-saving plans (e.g., Windows’ “Balanced” or “Power Saver” modes).
Read More:What Games Are Cpu Intensive – A Comprehensive Guide!
Undervolting:
- Reduce the voltage supplied to your CPU without affecting performance. Tools like Intel XTU or AMD Ryzen Master can help.
Limit Turbo Boost:
- Turbo Boost or Precision Boost allows CPUs to run at higher speeds temporarily. Disabling or limiting this feature can save power.
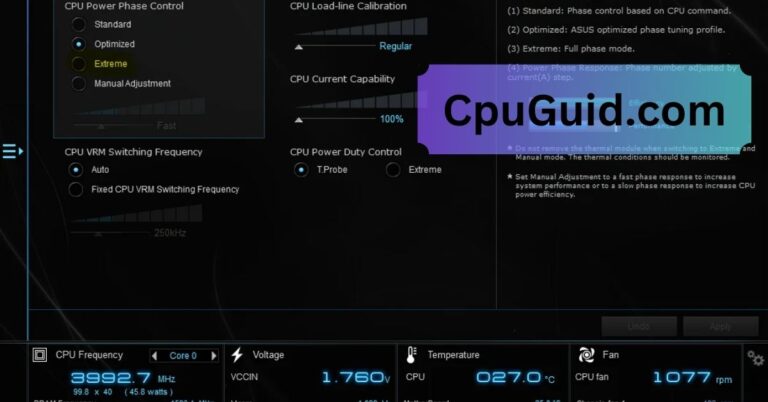
Adjust BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Use features like “Eco Mode” or manual voltage control to reduce power draw.
Efficient Cooling:
- Keeping your CPU cool with efficient cooling systems can prevent it from drawing extra power to compensate for high temperatures.
Turn Off Background Tasks:
- Close unnecessary programs and services to reduce CPU load.
The Impact of CPU Power Usage on Your System:
Power Supply Compatibility:
- Ensure your PSU can handle your CPU’s peak power consumption along with other components.
System Heat:
- High power usage generates more heat, requiring robust cooling solutions.
Battery Life (Laptops):
- For laptops, power-efficient CPUs translate to longer battery life. Disabling high-performance features when on battery can help conserve energy.
Environmental Impact:
- Lower power consumption reduces your system’s carbon footprint, making your setup more eco-friendly.
Read More:Do Cpu Come With Cooler – Everything You Need to Know!
Future Trends in CPU Power Efficiency:
The tech industry is continually working on improving CPU efficiency. Here’s what the future holds:
Smaller Nanometer Processes:
- As manufacturers move to smaller processes (e.g., 3nm and beyond), CPUs will become more power-efficient.
AI-Powered Power Management:
- Advanced algorithms will dynamically optimize power usage based on workloads.
Integration of ARM Architecture:
- ARM-based CPUs, like Apple’s M1 and M2 chips, are setting new benchmarks in power efficiency for both laptops and desktops.
FAQ’s
1. What is CPU power usage measured in?
CPU power usage, measured in watts (W), reflects the energy consumed during operation. It varies depending on processor type, workload, system configuration, and additional factors such as cooling and performance settings.
2. How does workload affect CPU power usage?
Power consumption increases significantly during intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or 3D rendering, as the CPU works harder, while lighter activities such as web browsing or document editing use considerably less power.
3. What tools can I use to monitor CPU power usage?
Real-time CPU power usage data can be monitored using tools such as HWMonitor, Core Temp, or Intel Power Gadget, which display energy consumption, temperature, and voltage details.
4. Does overclocking increase CPU power usage?
Overclocking increases clock speeds and voltage, which boosts CPU performance but also significantly raises power consumption and heat output.
5. Can optimizing power usage reduce system heat?
Lowering power consumption reduces heat output, enhancing cooling efficiency, protecting components, and extending the overall lifespan of your hardware.
Conclusion:
Understanding your CPU’s power usage is crucial for building and maintaining an efficient, high-performance computer system. By recognizing factors that affect power consumption—such as processor type, workload, and system configuration—and utilizing tools to measure and optimize it, you can boost system performance while controlling energy costs. Whether you’re a casual user or a power user, being mindful of CPU power usage promotes better energy efficiency and longevity, ensuring a balanced and sustainable computing experience for all users.