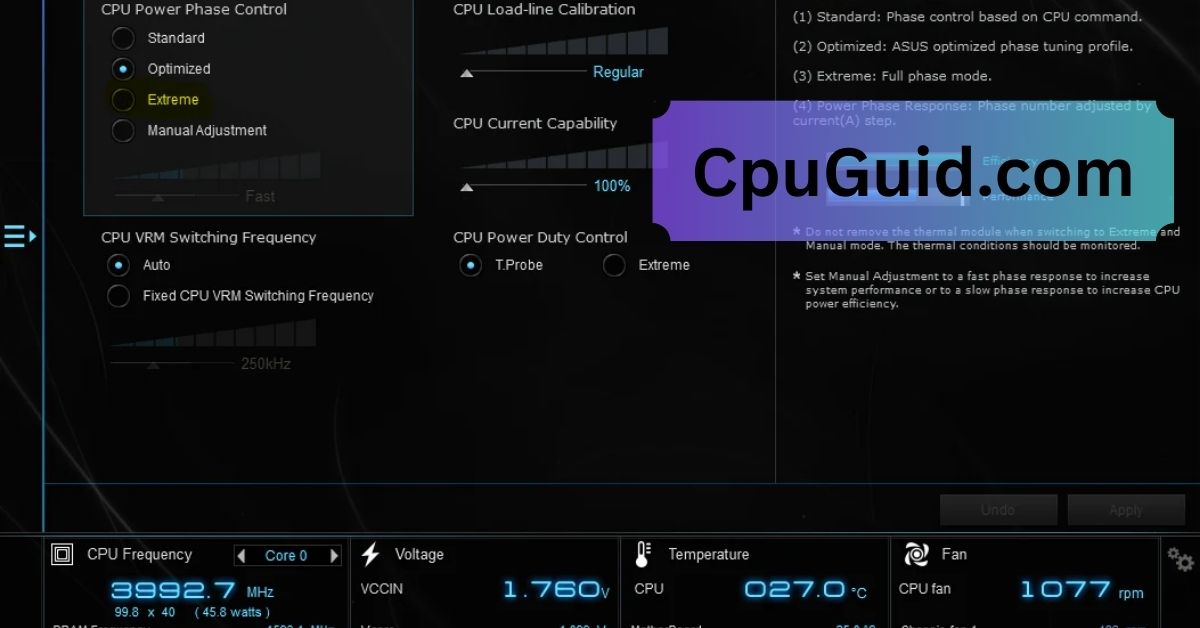
Cpu Power Phase Control – A Key to Enhanced Overclocking!
Learn about CPU power phase control, a critical feature that optimizes power delivery, enhances efficiency, and ensures stable performance for your CPU.
In this article, we explore CPU Power Phase Control and its impact on system performance. Learn how control optimizes energy efficiency and overclocking. Discover tips to improve CPU longevity with power management.
What Is CPU Power Phase Control?
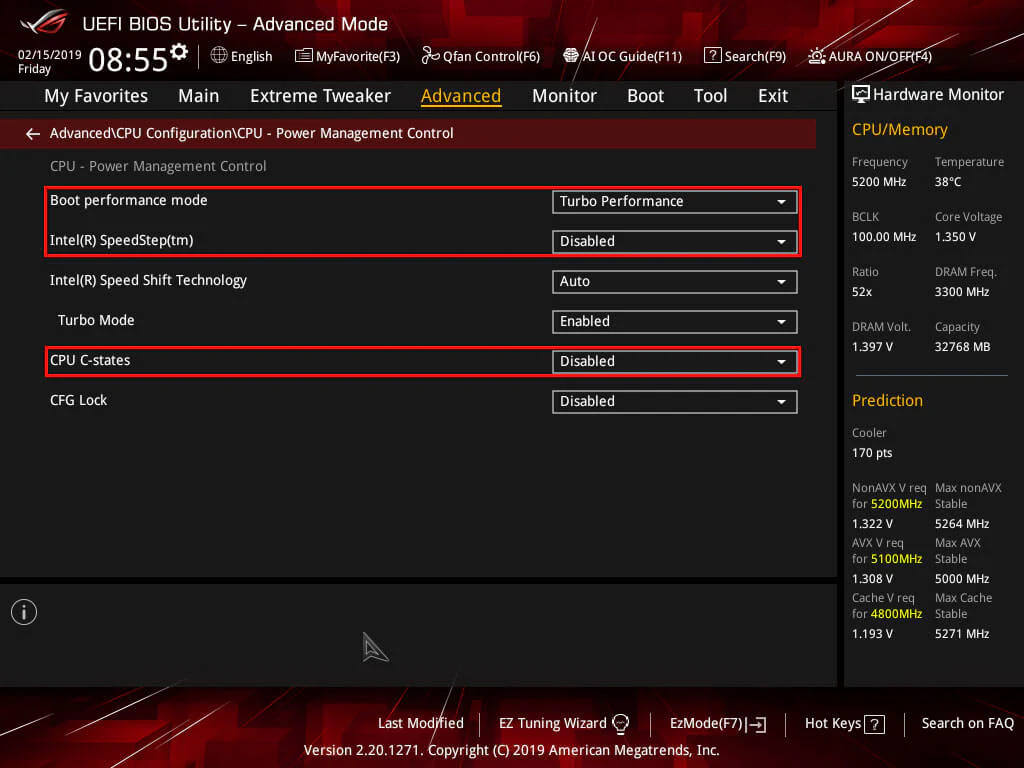
CPU power phase control is a technology embedded in motherboards that regulates how power is supplied to the central processing unit (CPU). It is part of the motherboard’s voltage regulation module (VRM), which converts the power from the power supply unit (PSU) into a stable and usable form for the CPU. The power phase control determines how many VRM phases are active at any given time, ensuring the right amount of power is delivered based on the CPU’s workload.
Modern CPUs are highly sensitive to fluctuations in power delivery. Without proper regulation, excessive power can lead to overheating and damage, while insufficient power can cause instability and crashes. CPU power phase control mitigates these risks by dynamically adjusting the power delivery.
How Does CPU Power Phase Control Work?
The VRM on a motherboard consists of multiple phases, each responsible for delivering a portion of the total power required by the CPU. The number of phases can range from a few to over a dozen in high-end motherboards. These phases work together to:
- Distribute the Load: Each phase shares the burden of power delivery, reducing stress and heat generation in individual components.
- Enhance Efficiency: By selectively enabling or disabling phases based on demand, the system optimizes power usage.
- Improve Stability: The even distribution of power helps maintain stable CPU performance, especially under heavy workloads like gaming or video rendering.
- CPU power phase control allows the motherboard to switch between different modes, such as:
- Phase Boosting: Activates additional phases during high-performance tasks to ensure adequate power delivery.
- Phase Shedding: Reduces the number of active phases during idle or low-load scenarios to conserve energy and reduce heat.
Benefits of CPU Power Phase Control:
1. Improved Performance:
When the CPU operates under heavy workloads, it requires a steady and ample supply of power. CPU power phase control ensures that the VRM can handle the demand, preventing performance bottlenecks caused by power limitations.
Read More: The Brain Of The Computer Is The Cpu – Key Insights!
2. Enhanced Efficiency:
By dynamically adjusting the active power phases, the system minimizes unnecessary energy consumption. This is especially beneficial for laptops and compact PCs where power efficiency is a priority.
3. Better Thermal Management:
Reducing the stress on individual VRM components helps lower heat generation. This not only keeps the system cooler but also extends the lifespan of the motherboard and CPU.
4. Longer Hardware Lifespan:
Stable and efficient power delivery reduces wear and tear on both the VRM and CPU, ensuring that your system remains reliable over time.
5. Overclocking Support:
For enthusiasts looking to push their systems beyond stock performance, CPU power phase control provides the stability required for safe and effective overclocking.
Key Features of CPU Power Phase Control Settings:
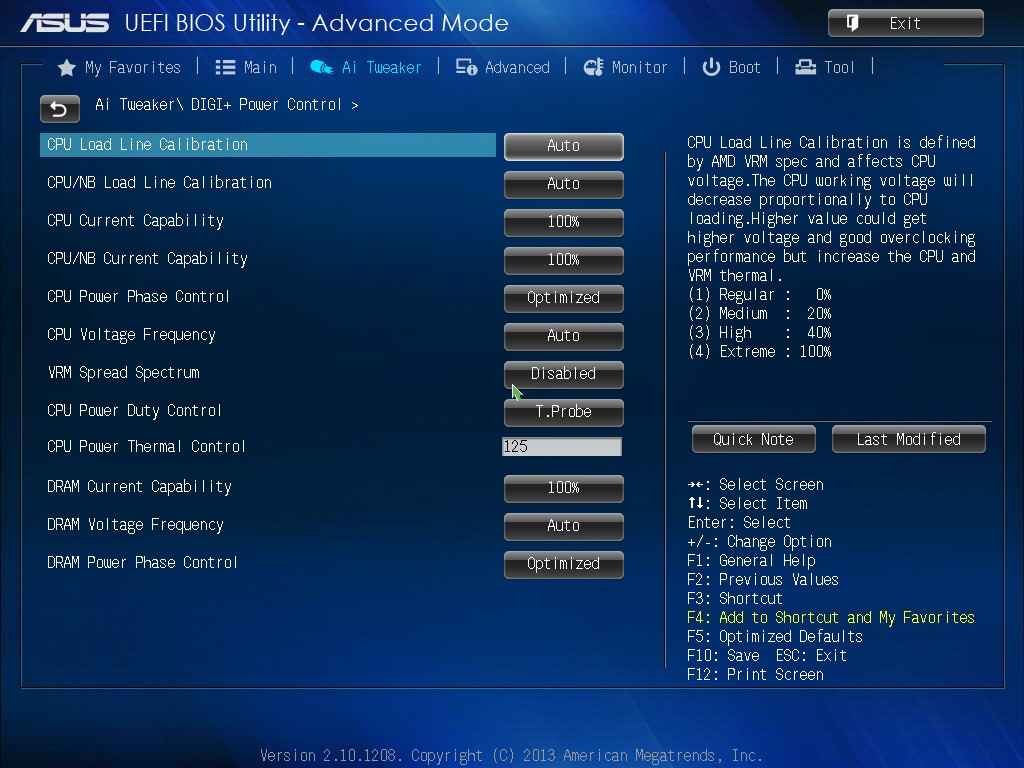
Most modern motherboards allow users to configure CPU power phase control through the BIOS or UEFI interface. Common settings include:
Auto Mode: Automatically adjusts phases based on workload, providing a balance between performance and efficiency.
Extreme Performance Mode: Activates all phases for maximum power delivery, ideal for overclocking and intensive tasks.
Eco Mode: Minimizes active phases to conserve energy and reduce heat output during low-demand scenarios.
Manual Configuration: Allows advanced users to fine-tune phase control settings for specific requirements.
Choosing the Right Motherboard for Power Phase Control:
When selecting a motherboard, the quality of its VRM and power phase control capabilities is crucial. Here are some factors to consider:
- Number of Phases: More phases generally provide better power distribution and stability. High-end motherboards often feature 12+ phases for optimal performance.
- Phase Doublers: Some motherboards use phase doublers to simulate additional phases, improving performance without increasing component count.
- Heat Management: Look for motherboards with robust heatsinks and cooling solutions for the VRM.
- BIOS Features: Ensure the motherboard offers user-friendly BIOS/UEFI settings for power phase customization.
Common Issues with CPU Power Phase Control and How to Address Them:
1. Overheating VRMs:
If the VRMs are overheating, consider improving airflow within your case or investing in better cooling solutions. High-quality thermal pads and heatsinks can also help.
2. Unstable Overclocking:
Inconsistent power delivery can cause instability during overclocking. Ensure that your motherboard’s VRM is robust enough to handle the increased demand.
3. Power Supply Limitations:
An inadequate PSU can hinder the performance of the VRM. Ensure your PSU has enough wattage and high efficiency to support your system.
Read More: How Much Power Does My Cpu Use – A Complete Guide!
Best Practices for Optimizing CPU Power Phase Control:
- Update BIOS/UEFI: Manufacturers often release updates to improve power phase control and overall stability.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring software to keep an eye on VRM and CPU temperatures.
- Test Different Settings: Experiment with phase control settings to find the best balance between performance and efficiency for your workload.
- Invest in Quality Components: Pairing a high-quality motherboard with a reliable PSU ensures stable power delivery.
FAQ’s
1. What is CPU power phase control?
CPU power phase control is a motherboard feature regulating power delivery to the CPU, ensuring stability, efficiency, and optimal performance across workloads.
2. Why is CPU power phase control important?
CPU power phase control prevents overheating, enhances power efficiency, and maintains system stability by dynamically managing power delivery across varying workloads.
3. How does CPU power phase control work?
Optimize CPU power phase control by exploring BIOS settings, investing in quality hardware, and ensuring proper cooling for reliable performance.
4. Can I configure CPU power phase control?
Modern motherboards enable BIOS/UEFI adjustments with modes such as Auto, Performance, and Eco, ensuring tailored power delivery and efficiency.
5. What should I consider when choosing a motherboard for power phase control?
CPU power phase control optimizes performance and efficiency. Explore BIOS settings, invest in quality hardware, and ensure cooling for consistent and reliable CPU performance.
Conclusion:
CPU power phase control is a vital yet underappreciated feature of modern hardware. Understanding and optimizing its settings can boost performance, efficiency, and hardware lifespan. Whether you’re a casual user or an overclocking enthusiast, exploring BIOS options, investing in a quality motherboard, and ensuring proper cooling can maximize results. With the right setup, your CPU will deliver reliable, consistent performance for years to come.