Cpu Machine Check Architecture Error Dump – A Comprehensive Guide!
Learn about CPU Machine Check Architecture (MCA) error dumps, their causes, and fixes to resolve hardware issues, prevent crashes, and enhance PC stability.
In this article, we explain CPU Machine Check Architecture (MCA) error dumps, their causes, and symptoms. Find troubleshooting tips to fix issues like overheating and hardware faults. Learn how to prevent future errors and keep your system stable.
What Is the CPU Machine Check Architecture?
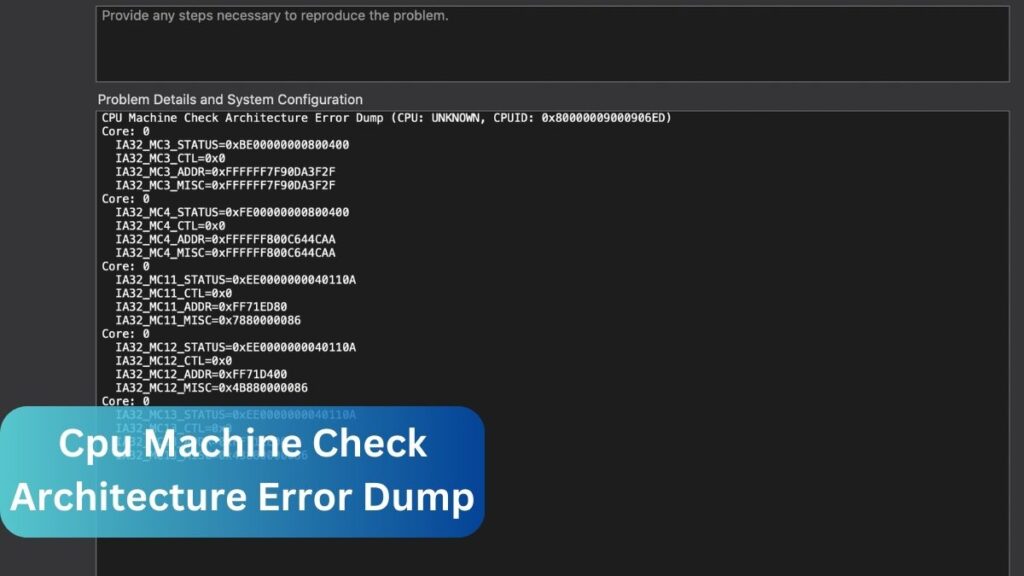
The Machine Check Architecture (MCA) is a diagnostic feature built into modern CPUs. Its primary purpose is to detect and report hardware errors, ensuring the system remains stable and functional. MCA is integral to maintaining the health of your computer, as it can preemptively identify potential hardware failures and log them for troubleshooting.
When an issue arises, the CPU generates a Machine Check Exception (MCE), which is logged as an MCA error dump. These error dumps provide crucial information for diagnosing problems related to hardware, firmware, or system configurations.
Why Does an MCA Error Occur?
Several factors can trigger an MCA error dump. Below are the most common causes:
1. Overheating Components:
The CPU and other components, such as the GPU, generate heat during operation. If the cooling system is inadequate or obstructed by dust, these components can overheat, leading to instability and MCA errors.
2. Faulty or Aging Hardware:
Hardware failures are a common cause of MCA errors. For instance:
- Defective RAM: Corrupted memory can disrupt data flow.
- Failing CPU: Physical or electrical damage can render the CPU unstable.
- Unreliable Storage Drives: Bad sectors or failing SSDs/HDDs can cause read/write errors.
3. Power Supply Issues:

Inconsistent power delivery from a faulty power supply unit (PSU) or power surges can lead to hardware malfunctions and MCA error logs.
4. BIOS/UEFI Problems:
An outdated or incorrectly configured BIOS/UEFI firmware may lead to compatibility issues between hardware and software, causing MCA errors.
5. Driver Conflicts or Software Bugs:
Device drivers act as intermediaries between the operating system and hardware. Corrupted, outdated, or incompatible drivers can cause miscommunication, triggering errors logged by the MCA system.
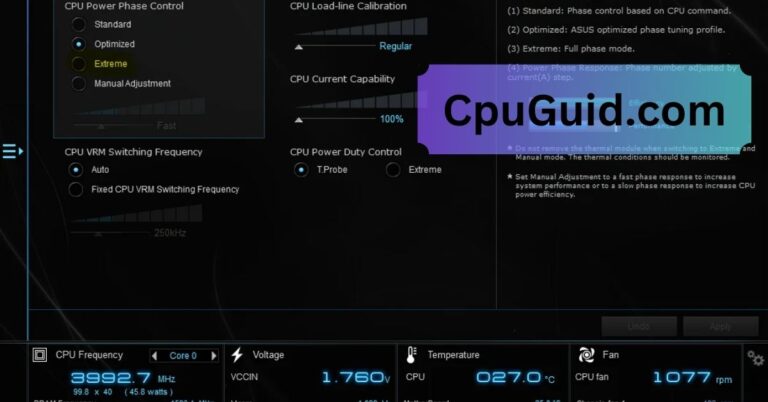
6. System Overclocking:
Pushing your CPU or GPU beyond their factory-specified limits may cause instability, leading to MCA errors as the system struggles to maintain performance.
Symptoms of a CPU MCA Error:
MCA errors often manifest through several warning signs, including:
- Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): Typically displaying error messages like “Machine Check Exception.”
- Sudden Reboots: The system may restart without warning.
- Crash Dumps: Error logs generated in Event Viewer or other diagnostic tools.
- Boot Failures: The system may struggle to start or load the operating system.
How to Troubleshoot and Resolve MCA Errors?
Resolving an MCA error requires a systematic approach to identify and address the underlying issue.
1. Analyze the Error Logs:
Start by examining the crash dumps or event logs:
- In Windows, access the Event Viewer and look for critical errors related to Machine Check Exceptions.
- Use third-party tools like WhoCrashed or BlueScreenView to interpret the error codes.
2. Inspect Hardware:
- Check RAM: Use diagnostic tools like MemTest86 to test your memory modules for errors.
- Inspect the CPU: Look for physical damage or thermal paste degradation.
- Test the PSU: Use a multimeter or PSU tester to ensure stable voltage output.
3. Update System Firmware and Drivers:
- Visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website to download the latest BIOS/UEFI updates.
- Use device manager or tools like Driver Booster to update drivers for hardware components.
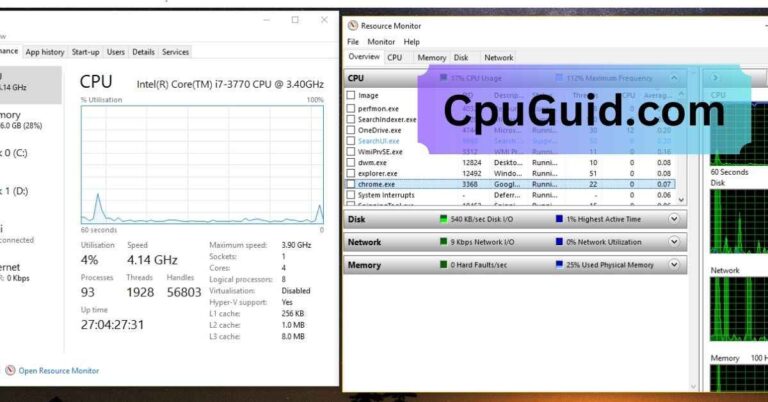
4. Monitor System Temperatures:
Download hardware monitoring tools such as HWMonitor, Core Temp, or Open Hardware Monitor to check CPU and GPU temperatures. Keep temperatures below 85°C for most processors under load.
5. Disable Overclocking:
If you’ve overclocked your CPU, revert to default settings via the BIOS/UEFI. Overclocking can strain components, leading to errors.
6. Run System Diagnostics:
- Most manufacturers provide diagnostic tools accessible from the BIOS/UEFI interface.
- Check for hardware faults using these built-in utilities.
7. Reinstall or Repair the Operating System:
If software corruption is suspected, reinstall the operating system or use the built-in repair tools to resolve potential driver or system file issues.
Advanced Troubleshooting Steps:
If basic troubleshooting does not resolve the issue, consider the following advanced steps:
1. Use Diagnostic Software:
Tools like Intel Processor Diagnostic Tool or AMD Ryzen Master Utility can perform detailed diagnostics on your CPU.
2. Replace Suspect Components:
If diagnostics indicate hardware failure, replace the faulty component. For example, defective RAM or an aging PSU should be swapped out.
3. Check for Firmware Updates Beyond BIOS:
Some components, like SSDs and GPUs, have their own firmware. Update these using tools provided by the manufacturer.
4. Consult a Professional:
If the issue persists, contact a certified technician for further analysis and potential hardware replacements.
How to Prevent MCA Errors in the Future?
Prevention is always better than cure. Follow these best practices to minimize the risk of MCA errors:
1. Regular Maintenance:
- Clean your system regularly to remove dust from fans, vents, and heat sinks.
- Replace thermal paste on the CPU every few years to maintain optimal cooling.
2. Invest in Quality Hardware:
- Purchase reliable components from reputable manufacturers to avoid premature failures.
3. Monitor Power Stability:
- Use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to protect against power surges and outages.
- Ensure your PSU provides adequate wattage for your system.
4. Keep Software Up-to-Date:
- Regularly update your operating system, drivers, and BIOS/UEFI firmware.
- Avoid using beta or unverified software unless necessary.
5. Avoid Aggressive Overclocking:
- While overclocking can boost performance, excessive adjustments can compromise hardware stability.
6. Enable System Monitoring:
- Install software to monitor system health, temperatures, and performance metrics. Early detection of anomalies can prevent major issues.
FAQ’s
1. What is a CPU Machine Check Architecture (MCA) error dump?
An MCA error dump is a diagnostic report generated by the CPU to log hardware-related errors, such as overheating, power issues, or faulty components, detected by the Machine Check Architecture.
2. What causes an MCA error dump?
Common causes include overheating components, defective hardware (e.g., RAM or CPU), power supply fluctuations, outdated BIOS/UEFI, or driver conflicts.
3. How can I fix an MCA error dump?
You can resolve it by checking hardware health, updating BIOS and drivers, monitoring system temperatures, disabling overclocking, and repairing or reinstalling the operating system if necessary.
4. Can an MCA error dump permanently damage my computer?
No, the error itself doesn’t cause damage. However, it indicates underlying issues that, if unaddressed—like overheating or power instability—could harm your hardware.
5. How can I prevent MCA errors in the future?
Maintain your system with regular cleaning, use quality hardware, ensure proper cooling, update firmware and drivers regularly, and avoid excessive overclocking.
Conlusion: Cpu Machine Check Architecture Error Dump!
Encountering a CPU Machine Check Architecture Error Dump can be a frustrating experience, but with a clear understanding of its causes and solutions, you can address the issue effectively. By following the troubleshooting steps and adopting preventive measures, you’ll enhance your system’s stability and performance, reducing the likelihood of future errors.