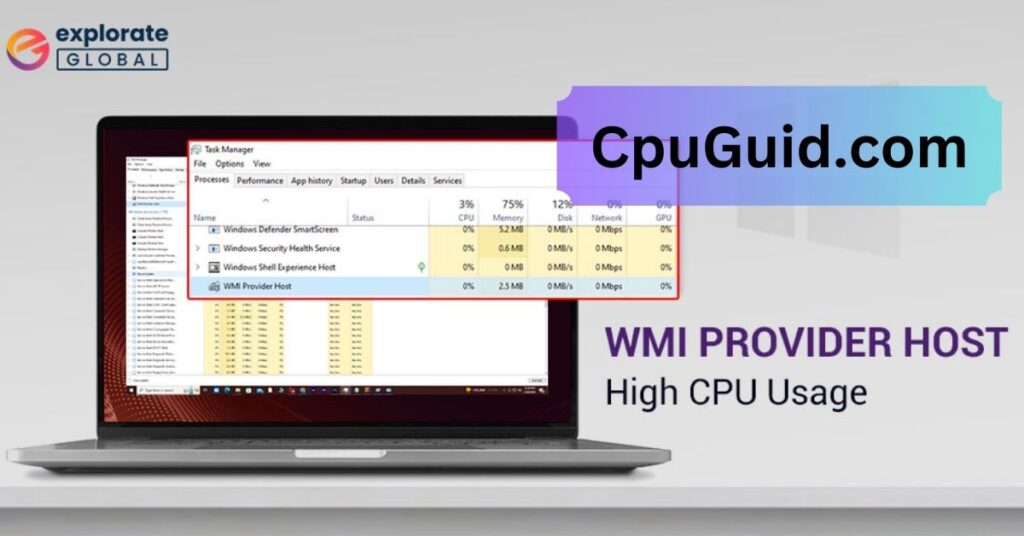
Wondering if 60°C is safe for your CPU? Learn why this temperature is safe for your processor and how to maintain optimal cooling for better performance and longevity.
In this article, we explore whether a CPU temperature of 60°C is safe, explaining the ideal temperature ranges for processors. We also provide tips on how to manage and maintain optimal cooling for better performance and longevity. Learn everything you need to know to keep your CPU running safely and efficiently.
What is the Normal Temperature Range for a CPU?
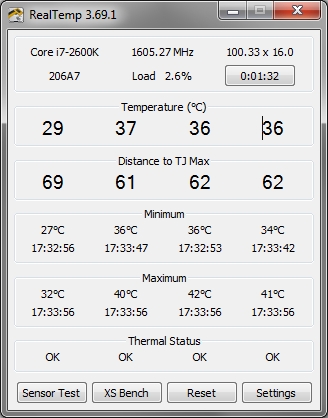
Before answering the question of whether 60°C is safe, it’s important to understand what temperature range is considered normal for a CPU. The performance of processors is heavily influenced by their temperature, as they can experience thermal throttling or even permanent damage when they become too hot.
- Idle Temperature: When your computer is idle or performing light tasks like browsing the web or watching videos, the CPU should typically operate at temperatures ranging between 30°C and 50°C. This ensures that the processor is not overheating when not under load.
- Under Load: When you’re running resource-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or running complex applications, the CPU temperature will naturally rise. During such activities, temperatures between 50°C and 70°C are generally acceptable and considered safe. This includes 60°C, which is on the lower end of the acceptable spectrum.
- Critical Temperature: Most modern CPUs are designed to handle higher temperatures, with maximum safe operating temperatures ranging between 85°C and 100°C depending on the model. Once a CPU approaches these temperatures, it could trigger automatic thermal throttling to prevent permanent damage, and performance may decrease significantly. Sustained temperatures above this range can cause long-term damage and potentially shorten the lifespan of the processor.
Is 60°C Safe for a CPU?
Yes, 60°C is considered safe for a CPU under most circumstances, particularly during high-demand tasks. However, it is essential to keep in mind that this temperature is on the upper end of the normal operating range for many processors.
Here’s a breakdown of why 60°C is generally safe:
- Modern CPU Design: Most modern processors, including Intel and AMD chips, are designed to operate safely at temperatures as high as 90°C to 100°C. These processors come with built-in thermal throttling mechanisms that automatically reduce their clock speeds to avoid damage when the temperature rises too high. Therefore, 60°C is well below the critical limit, which makes it a safe operating temperature.
- Thermal Throttling: If your CPU temperature reaches dangerous levels (typically above 90°C), the processor will begin to throttle its performance to reduce heat generation. This results in reduced system performance, but it also protects your hardware from thermal damage. Since 60°C is far below the critical temperature, it won’t trigger throttling or performance degradation.
- Sustained Usage: For most users, a CPU temperature of 60°C will not cause any issues, even with sustained usage during gaming, content creation, or multitasking. As long as the temperature doesn’t continue to rise uncontrollably or frequently reach high levels, the CPU should function efficiently.
Read More:http://Why Is My Cpu Overclocking Itself – Causes and Fixes Explained!
What Could Cause a CPU to Reach 60°C?
Understanding the factors that influence CPU temperature is important when managing heat levels. Several elements can cause your CPU to reach or exceed 60°C, including:
- Heavy Workloads: Running demanding software applications like video editors, 3D rendering programs, or high-end video games will stress the CPU and increase its temperature.
- Poor Cooling Solutions: Inadequate cooling solutions, such as low-quality thermal paste, inefficient heatsinks, or poorly functioning cooling fans, can cause the CPU temperature to rise. Airflow within the case is also a critical factor in regulating heat.
- Ambient Temperature: The temperature of your room or environment can also play a role in CPU temperature. If you’re working in a warm room or without air conditioning, the temperature inside the case could rise, pushing the CPU to higher levels.
- Overclocking: Overclocking is the practice of increasing a CPU’s clock speed beyond the manufacturer’s specified limits. This raises the processor’s power consumption and increases the amount of heat it generates, causing temperatures to rise above the usual range.
- Dust and Debris: Over time, dust and debris can accumulate inside your computer case, especially on cooling components like fans and heatsinks. This can reduce airflow and heat dissipation, leading to higher temperatures.
How to Keep Your CPU Temperature Safe?
If you want to ensure your CPU stays within a safe operating range, here are some tips and best practices:
- Improve Case Airflow: Proper airflow within your computer case is essential for cooling. Ensure there are intake and exhaust fans working effectively to move air in and out of the case. You may also want to use cable management techniques to avoid obstructing airflow.
- Upgrade Cooling Solutions: If your CPU temperature regularly exceeds 60°C during heavy use, it may be time to upgrade your cooling system. Consider investing in a high-quality air cooler or a liquid cooling solution. These cooling systems are designed to improve heat dissipation and maintain a lower CPU temperature.
- Replace Thermal Paste: Thermal paste is applied between the CPU and the heatsink to help transfer heat more efficiently. Over time, thermal paste can dry out or degrade, reducing its effectiveness. Replacing thermal paste can help reduce the temperature of your CPU.
- Clean the Interior: Dust buildup on cooling components and vents can block airflow, causing the system to overheat. Regularly clean the interior of your computer using compressed air to remove dust and debris.
- Monitor CPU Temperature: Use software tools such as Core Temp, HWMonitor, or MSI Afterburner to monitor your CPU temperature in real-time. These tools will help you keep track of temperature fluctuations and ensure that your processor stays within a safe range.
- Consider Undervolting or Lowering Clock Speeds: If you’re overclocking your CPU, you can reduce the voltage or adjust the clock speeds to lower power consumption and reduce heat generation. This can help maintain a cooler CPU temperature during demanding tasks.
FAQ’s
- Is 60°C too hot for a CPU?
No, 60°C is generally safe for a CPU under load. Modern processors can handle temperatures between 50°C and 70°C without causing damage or affecting performance.
- What temperature is ideal for a CPU?
The ideal temperature for a CPU is typically between 30°C and 50°C when idle, and between 50°C and 70°C under heavy load.
- At what temperature does CPU throttling occur?
CPU throttling usually occurs when temperatures reach around 90°C to 100°C. At these levels, the processor reduces performance to avoid overheating.
- Can a CPU run at 60°C continuously?
Yes, a CPU can safely run at 60°C during sustained heavy use, such as gaming or video editing, as long as it doesn’t exceed higher critical temperatures.
- How can I lower my CPU temperature?
Improving case airflow, upgrading cooling systems, cleaning dust, and replacing thermal paste are effective ways to reduce CPU temperature and maintain optimal performance.
Conclusion:
To sum up, 60°C is generally safe for a CPU, especially under load during intensive tasks. Modern processors are built to handle higher temperatures and have built-in safety mechanisms like thermal throttling to prevent damage. However, it’s always wise to keep an eye on your CPU temperature, especially if it consistently approaches or exceeds 70°C. By ensuring proper cooling, airflow, and regular maintenance, you can prolong the life of your CPU and avoid potential overheating issues.