Learn how a motherboard can bottleneck a CPU and impact performance. Discover key factors and tips to avoid limitations.
In this article, we explore whether a motherboard can bottleneck a CPU and how it affects overall performance. We discuss key factors like chipset limitations, power delivery, and memory compatibility. Learn practical tips to choose the right motherboard and build a balanced system.
What Does Bottleneck Mean?
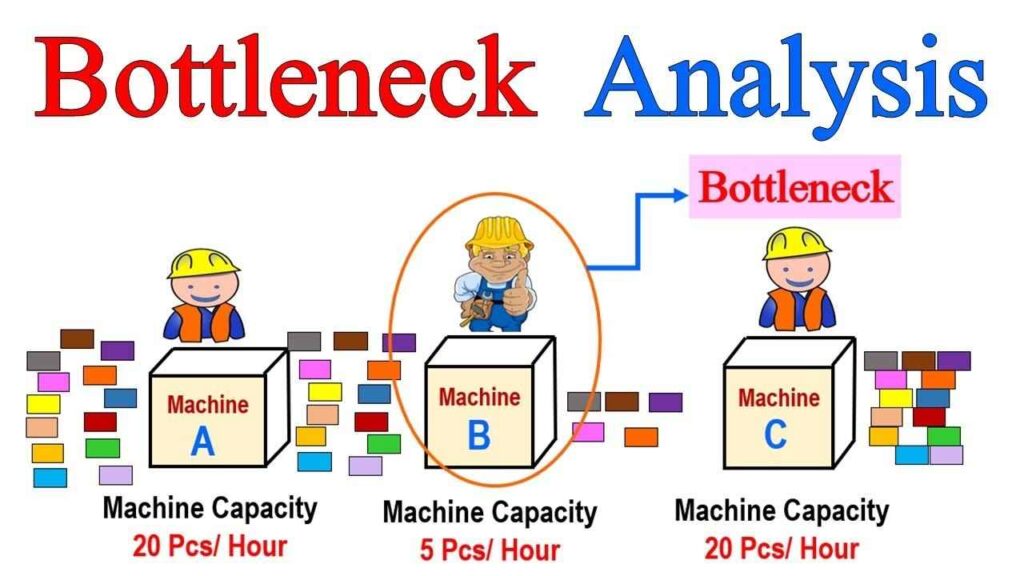
Before we get into the motherboard’s role, let’s clarify what a bottleneck is. A bottleneck occurs when one component in a system limits the performance of another. In the context of CPUs and motherboards, this typically means that the motherboard’s limitations prevent the CPU from operating at its full potential.
How a Motherboard Can Bottleneck a CPU?
A motherboard can bottleneck a CPU in various ways. Below are some of the most common factors that could create such a situation:
1. Incompatible Socket Type:
The CPU and motherboard must share the same socket type for them to work together. For instance, an Intel Core i7-13700K requires a motherboard with an LGA 1700 socket. Attempting to use a motherboard with a different socket will make installation impossible, effectively creating a bottleneck at the most basic level.
2. Chipset Limitations:
The chipset on a motherboard determines the features and functionalities it supports. A low-end chipset might not support overclocking, higher memory speeds, or certain PCIe configurations, which can limit the performance of high-end CPUs. For example:
- Pairing an Intel Core i9 with an entry-level H610 chipset may restrict the CPU’s overclocking potential and reduce access to advanced features.
- On AMD systems, using a Ryzen 9 processor with an A320 motherboard could similarly restrict performance due to lack of support for PCIe 4.0 or advanced power delivery.
3. Power Delivery (VRM Quality):
The voltage regulator module (VRM) on a motherboard manages power delivery to the CPU. High-performance CPUs demand robust power delivery systems. If the VRM is of poor quality or inadequate for the CPU’s power requirements, the system may throttle CPU performance to prevent instability or overheating.
Read More: Is 70c Hot For A Cpu – Understanding Safe Temperatures!
4. Memory Compatibility:
The motherboard determines the type and speed of RAM you can use. If your motherboard only supports DDR4 RAM at lower frequencies (e.g., 2400 MHz), but your CPU performs best with DDR4-3200 MHz, the slower memory speed will act as a bottleneck.
5. PCIe Lane Limitations:
Modern CPUs and GPUs rely on PCIe lanes for communication. High-performance CPUs support more PCIe lanes for tasks like multi-GPU setups or faster storage options. If your motherboard doesn’t support the same PCIe version as your CPU or offers fewer lanes, the system’s overall performance can be hampered.
6. BIOS Compatibility:
Sometimes, a motherboard may not support the latest CPUs out of the box because it lacks an updated BIOS. This can prevent the CPU from functioning at all or restrict its capabilities until the BIOS is updated.
Signs That Your Motherboard Is Bottlenecking Your CPU:
If you suspect a motherboard bottleneck, here are some common signs:
- Inconsistent Performance: Tasks that should be CPU-intensive, like gaming or video editing, may not show expected results.
- No Overclocking Options: If your CPU is unlocked but your motherboard doesn’t allow overclocking, you’re not getting the most out of your processor.
- Lower RAM Speeds: Your system fails to reach the advertised speeds of your RAM due to motherboard limitations.
- System Instability: Inadequate power delivery from the VRM can cause crashes, reboots, or throttling.
How to Avoid a Motherboard Bottleneck?
To ensure your CPU and motherboard work harmoniously, consider the following tips:
1. Match the Socket and Chipset:
Always verify that the motherboard’s socket and chipset are compatible with your chosen CPU. Manufacturers like Intel and AMD provide detailed specifications for their processors, including recommended chipsets.
2. Choose the Right Chipset:
Opt for a motherboard chipset that matches your use case. For example:
- For gaming, look for chipsets that support high-speed PCIe lanes and memory overclocking.
- For workstation tasks, prioritize motherboards with robust VRMs and multi-GPU support.
3. Check VRM Quality:
Research motherboard reviews to evaluate the quality of the VRM. Premium motherboards often come with better VRMs that support stable performance even under heavy CPU loads.
4. Consider Future Upgrades:
Invest in a motherboard that supports future technologies and upgrades, such as DDR5 RAM or PCIe 5.0. This ensures your system remains relevant longer.
Read More: Microcenter 25 Off Cpu – Tips and Tricks!
5. Update the BIOS:
Keep your motherboard’s BIOS up-to-date to ensure compatibility with newer CPUs and features.
Examples of Ideal CPU-Motherboard Pairings:
Here are a few examples of CPU and motherboard pairings to avoid bottlenecks:
- Intel Core i5-13600K with a Z790 chipset motherboard: Allows overclocking and supports DDR5 memory.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D with a B650 or X670 chipset motherboard: Supports PCIe 5.0 and fast memory.
FAQ’s
1. What is a motherboard bottleneck?
A motherboard bottleneck occurs when its compatibility, features, or limitations restrict the CPU’s performance, preventing it from operating at its full potential and impacting overall system efficiency.
2. Can a low-quality VRM cause a bottleneck?
Inadequate VRMs on a motherboard lead to poor power delivery, which can cause CPU throttling, system instability, or inconsistent performance, especially during demanding tasks or under heavy workloads.
3. Does the chipset matter for CPU performance?
The chipset significantly influences overclocking potential, memory compatibility, PCIe version support, and overall system performance, ensuring seamless functionality and optimal hardware interaction in a computer.
4. Can an outdated BIOS bottleneck a CPU?
An outdated BIOS may lack support for newer CPUs, potentially limiting their performance or causing compatibility and operational issues.
5. How can I avoid a motherboard bottleneck?
Match the motherboard\u2019s socket, chipset, and features with your CPU’s requirements and update the BIOS regularly.
Conclusion:
While motherboards don’t directly impact raw CPU performance, their features, quality, and compatibility can significantly influence how well your CPU performs. Ensuring your motherboard is up to the task involves choosing one that matches your CPU’s specifications, power requirements, and intended use case. By understanding the potential for a motherboard to bottleneck a CPU and taking proactive measures, you can build a balanced and efficient system that delivers the performance you need.