Why Is Cpu Frequency So High – Common Causes Explained!
Learn why your CPU frequency may be high and how it impacts performance. Discover common causes, including Turbo Boost, overclocking, and cooling issues.
This article aims to explain why your CPU frequency could be higher than expected, what it means for your system, and how to manage it effectively. We’ll dive into technical aspects in a simplified way, making sure to address common concerns for both beginners and seasoned users.
What is CPU Frequency?
Before we explore why the CPU frequency might be high, let’s quickly define what CPU frequency means.
The CPU frequency (measured in GHz or gigahertz) refers to the speed at which your processor executes tasks. It is the number of cycles (or operations) the CPU can perform per second. A higher frequency generally means faster performance, but it’s not the sole determinant of your CPU’s power. Other factors, like core count, architecture, and thermal conditions, also play a crucial role.
Why Does CPU Frequency Change?
A common misconception is that a CPU runs at a constant frequency, but in reality, it can fluctuate based on several factors. Here are the most significant reasons why the CPU frequency may be higher than expected:
1. CPU Boost Technology (Turbo Boost):
Many modern processors, including Intel’s Turbo Boost and AMD’s Precision Boost, are designed to automatically increase the CPU frequency under certain conditions. These technologies allow the processor to run at a higher frequency temporarily to provide additional power when needed, such as during gaming, video editing, or other intensive tasks.
When your system detects a demanding task, it will temporarily raise the CPU frequency to improve performance. However, this boost is not permanent and is only active as long as the system requires it. After the demand decreases, the CPU returns to its normal base frequency.
2. High Workload and Task Demands:
If you’re running resource-intensive applications or performing complex tasks such as gaming, 3D rendering, video editing, or compiling large programs, the CPU frequency will increase to handle the workload. During such tasks, the processor needs to perform more cycles per second, which can result in a noticeable rise in frequency.
Even running multiple applications or browser tabs at once can push your CPU’s frequency higher. If your device is doing many things at once, the CPU will automatically adjust to ensure smooth performance.
Read More: Is Anti Aliasing Cpu Or Gpu – A Detailed Comparison!
3. Background Processes and Applications:
Even if you think your computer is idle, many background processes, services, and updates are running behind the scenes. These tasks can raise CPU usage and, subsequently, the frequency. Antivirus scans, system updates, and cloud-syncing services often use CPU resources without your direct input.
It’s a good idea to monitor what’s running in the background to determine whether any unnecessary tasks are consuming CPU power and potentially causing a high frequency.
4. Power Settings and Performance Modes:
Many operating systems allow users to choose different power settings, such as “Balanced,” “Power Saver,” or “High Performance.” In the High-Performance mode, your CPU is likely to operate at higher frequencies to ensure responsiveness and speed. This setting can make your laptop or desktop run faster, but it will also consume more power, especially in laptops.
The CPU frequency can be adjusted based on the system’s power plan. If you’re using a power-saving plan, the CPU might throttle down its frequency to conserve battery or reduce heat. Switching to a higher performance setting will allow the CPU to run at higher frequencies when required.
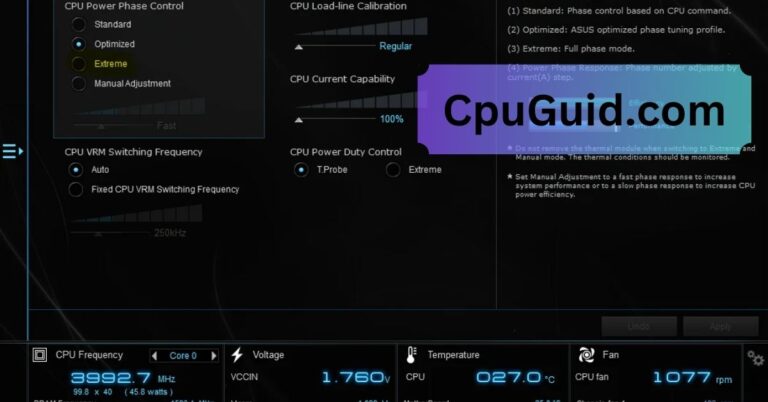
5. Overclocking:
Overclocking refers to manually increasing the clock speed of your CPU beyond its stock frequency to enhance performance. This is usually done by enthusiasts or gamers looking to push their hardware to its limits.
Overclocking can result in higher-than-normal CPU frequencies. However, it also increases power consumption and generates additional heat, so it’s important to monitor the system’s temperature and ensure adequate cooling when overclocking.
If your CPU frequency is high and you haven’t overclocked it yourself, it might be worth checking whether any automatic overclocking settings (such as Intel’s Turbo Boost or AMD Precision Boost) have been activated.
6. Temperature and Cooling Conditions:
The temperature of your CPU directly impacts its performance. A CPU running at high temperatures might throttle down its frequency to prevent overheating. However, in some cases, an improperly configured cooling system or inadequate airflow can lead to higher-than-normal CPU frequencies, as the processor attempts to maintain performance.
If your CPU is running at a high frequency but also seems unusually hot, it’s a good idea to check your system’s cooling system, including the CPU cooler, thermal paste, and airflow.
7. BIOS Settings and Firmware Updates:
In some cases, your system’s BIOS or UEFI settings can influence CPU behavior. Overzealous power-saving settings or outdated firmware could force the CPU into higher frequencies unexpectedly. Ensure that your BIOS is up-to-date and check your power settings to avoid unnecessary frequency spikes.
Is a High CPU Frequency Bad for Your System?
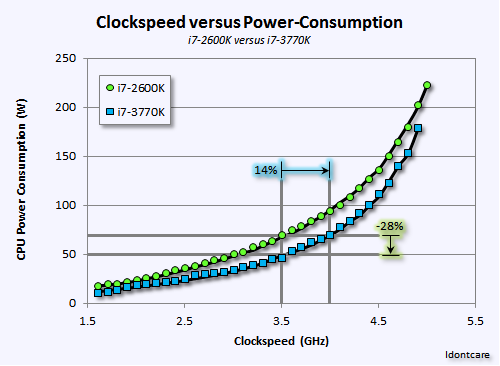
In general, a high CPU frequency is not inherently harmful if your system is designed to handle it. However, there are a few potential downsides to keep in mind:
- Increased Power Consumption: Running at higher frequencies will draw more power, which can be especially problematic for battery life on laptops.
- Increased Heat Production: A higher frequency generates more heat, which could result in thermal throttling or reduced CPU lifespan if cooling is inadequate.
- System Stability: Overclocking or having unstable power settings might lead to system instability, crashes, or data loss.
If you’re concerned about frequent spikes in CPU frequency, it might be a good idea to invest in better cooling solutions or tweak your power settings.
How to Monitor and Manage CPU Frequency?
Here are some steps to help monitor and manage your CPU frequency:
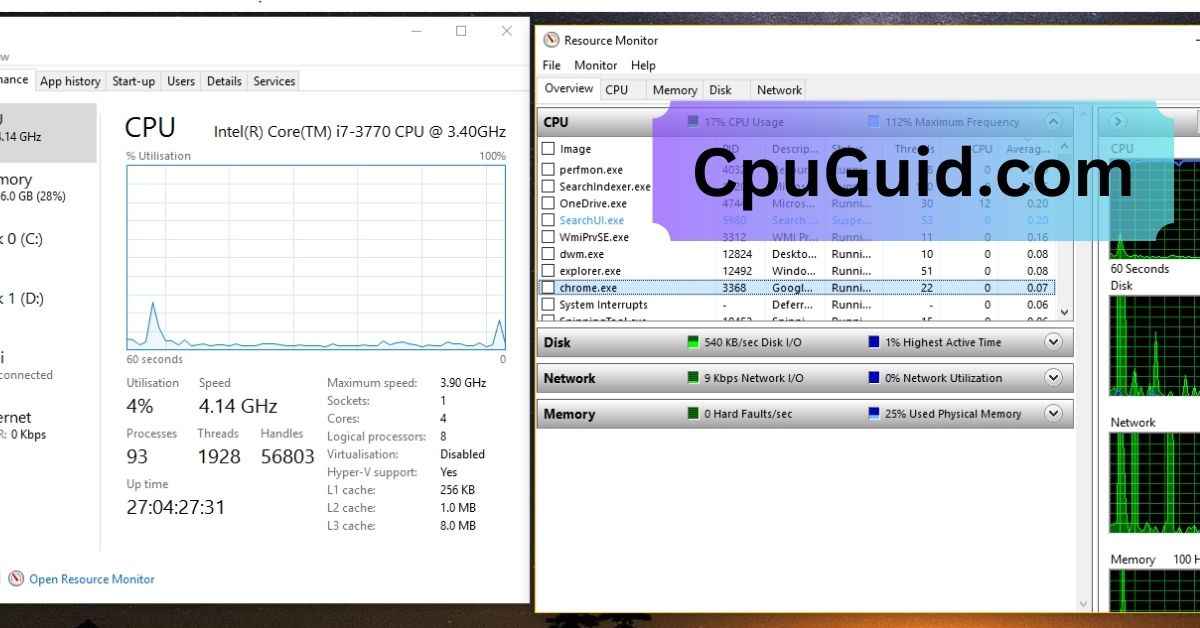
1. Task Manager (Windows):
On Windows, Task Manager offers a simple way to view CPU usage and frequency. You can open it by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc, and under the “Performance” tab, you can see the real-time CPU frequency and utilization.
2. System Preferences (macOS):
For Mac users, the “Activity Monitor” app allows you to monitor CPU usage and check for any processes consuming excessive CPU resources.
3. Third-Party Software:
For advanced users, tools like CPU-Z, HWMonitor, or Core Temp can provide in-depth details about your CPU’s frequency, temperature, and power usage. These tools are great for monitoring overclocking and thermal conditions.
Read More: Is 4000rpm Too Low For Cpu Fan – A Comprehensive Guide!
4. Adjust Power Settings:
In your system’s power settings, you can switch between performance modes. On Windows, go to “Control Panel” > “Power Options,” and choose a power plan that suits your needs. On macOS, navigate to “System Preferences” > “Energy Saver.”
5. Cooling Solutions:
Make sure your CPU cooling solution is sufficient for your needs. Consider upgrading your cooling system or adding additional fans to improve airflow, especially if you experience thermal throttling.
FAQ’s
1. What triggers a CPU frequency boost?
A CPU frequency boost is triggered when the processor detects a high-performance requirement, such as running intensive applications like games or video editors. Technologies like Intel Turbo Boost or AMD Precision Boost temporarily increase the frequency for better performance.
2. How does the cooling system impact CPU frequency?
An inadequate cooling system can cause the CPU to operate at a higher frequency to maintain performance, leading to excess heat. Conversely, proper cooling can help keep the CPU at optimal frequencies without thermal throttling.
3. Does CPU frequency always correlate with better performance?
Not necessarily. While a higher frequency can improve performance, it’s not the only factor. The number of cores, cache size, and CPU architecture also significantly impact overall system performance.
4. Can running multiple applications cause high CPU frequency?
Yes, running several applications or processes simultaneously increases the workload on the CPU. To handle the increased demand, the CPU may automatically raise its frequency to ensure smooth performance.
5. How can I manage high CPU frequencies on my system?
You can manage high CPU frequencies by adjusting your system’s power settings, disabling unnecessary background processes, or upgrading your cooling system. Monitoring tools like Task Manager or third-party software can also help identify processes that may be causing higher-than-normal frequencies.
Conclusion: Should You Worry About High CPU Frequency?
In most cases, a high CPU frequency is not a cause for concern, especially when it’s due to performance boosting. However, if the high frequency is consistent or excessive, especially when paired with elevated temperatures, it could signal problems with your system’s cooling, power settings, or overclocking. It’s important to monitor these factors to ensure your system remains stable and efficient.