Discover why your CPU may be overclocking itself, from automatic features to processes. Learn solutions to manage performance and prevent overheating.
In this article, we explore the reasons behind your CPU overclocking itself, including automatic features and background processes. We provide insights on how to monitor performance and temperature effectively. Additionally, you’ll find practical solutions to manage overclocking and ensure a stable computing experience.
What Is CPU Overclocking?
Overclocking a CPU involves increasing its clock rate beyond the manufacturer’s specifications, allowing it to process more instructions per second. This practice can lead to noticeable improvements in gaming performance, video editing, and other demanding applications. However, overclocking comes with risks, including increased heat output, power consumption, and the potential for reduced hardware lifespan if not managed properly.
The Basics of CPU Clock Speed:
Every CPU operates at a base clock speed measured in gigahertz (GHz), which indicates how many cycles it can perform in one second. Overclocking raises this speed, which can enhance performance but requires a careful balance to prevent overheating and instability.
How Does Overclocking Work?
Overclocking typically involves adjusting settings in the computer’s BIOS/UEFI or using specialized software. Users can modify various parameters, including:
- Core Voltage (Vcore): Increasing this can stabilize higher clock speeds but can also lead to higher temperatures.
- Clock Multiplier: This determines the CPU’s speed by multiplying the base clock frequency.
- Base Clock (BCLK): This is the foundational clock speed from which the CPU derives its operating frequency.
Why Is My CPU Overclocking Itself?
If you notice your CPU frequently reaching higher speeds than expected, several factors could contribute to this self-overclocking behavior.
1. Automatic Overclocking Features:
Modern CPUs and motherboards are equipped with automatic overclocking technologies that intelligently adjust clock speeds based on workload demands.
- Intel Turbo Boost Technology: This feature allows Intel processors to automatically increase their clock speed to improve performance during demanding tasks. When the CPU is under load and thermally capable, Turbo Boost kicks in to enhance performance without manual configuration.
- AMD Precision Boost: Similar to Intel’s technology, AMD’s Precision Boost dynamically adjusts clock speeds based on power and thermal conditions, providing extra performance during high-demand scenarios.
These features are designed to provide optimal performance while maintaining system stability, but they can lead to unexpected clock speed increases.
2. Overzealous BIOS/UEFI Settings:
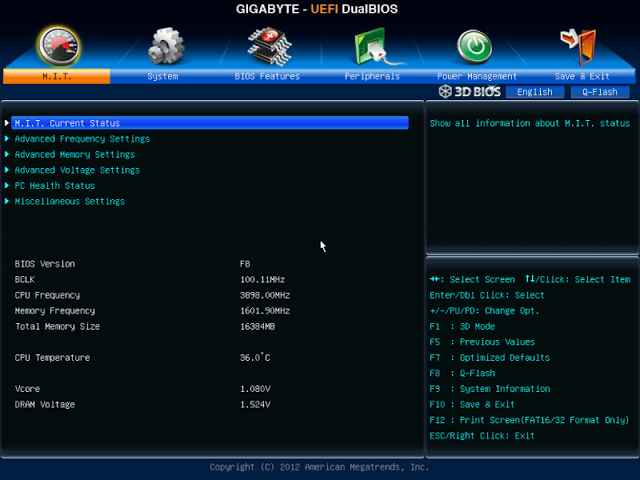
:Sometimes, users may inadvertently enable automatic overclocking settings within the BIOS/UEFI. Options such as “XMP profiles” for RAM or “automatic overclocking” features can lead to unexpected performance boosts.
To check and adjust these settings:
Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI setup by pressing the designated key (usually F2, Delete, or Esc) during boot.
Look for options related to CPU settings, performance modes, or automatic overclocking and adjust them according to your preferences.
3. Background Processes and Workloads
Certain applications can trigger temporary CPU overclocking. High-demand software, such as video rendering programs, 3D modeling applications, and modern games, can push the CPU to operate at higher clock speeds to accommodate increased load.
Identifying Resource-Heavy Applications:
Use Task Manager on Windows or Activity Monitor on macOS to identify which applications consume the most CPU resources.
Investigate these applications to determine if they require frequent adjustments to system performance.
4. Thermal Throttling and Cooling Solutions:
Inadequate cooling can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its performance to prevent overheating.
- Thermal paste: Ensure that thermal paste between the CPU and cooler is applied correctly and is not dried out. Reapplying high-quality thermal paste can improve heat dissipation.
- Cooling solutions: Consider upgrading your cooling system if your CPU frequently reaches high temperatures. Options include:
- Air Coolers: High-performance air coolers with larger heatsinks and more powerful fans.
- Liquid Cooling Systems: All-in-one (AIO) liquid coolers or custom liquid cooling setups can offer superior cooling performance.
5. Malware or Viruses:
Malicious software can cause erratic system behavior, including unintended CPU overclocking. Malware may create background processes that put undue stress on the CPU.
Preventive Measures:
Regularly scan your system with reputable antivirus software to detect and remove potential threats.
Use tools like Malwarebytes or Windows Defender for thorough scans.
6. Outdated Drivers or Software Conflicts
Outdated drivers can lead to performance issues, including unexpected CPU behavior. Compatibility issues may arise from outdated software, affecting how the CPU manages processes.
Maintaining Software Updates:
Ensure your operating system is updated, as many updates include important security and performance patches.
Check for driver updates for your CPU, GPU, and motherboard, which can typically be found on the manufacturer’s website.
7. Power Supply Issues

An inadequate or failing power supply unit (PSU) can cause instability in system performance, potentially leading to unexpected CPU behavior.
Ensure your PSU meets the recommended wattage for your components, particularly if you have added hardware recently.
Consider upgrading to a high-quality PSU if your current unit is several years old or of low quality.
How to Manage CPU Overclocking:
If your CPU is overclocking itself and you wish to manage this behavior, consider the following strategies:
1. Check BIOS/UEFI Settings:
Review and modify your BIOS settings to disable any automatic overclocking features.
Look for options such as “Auto Overclock” or “Performance Boost” and turn them off if you prefer a stable clock speed.
2. Monitor CPU Temperatures:
Utilize software tools such as HWMonitor, Core Temp, or MSI Afterburner to track CPU temperatures.
If you notice that temperatures consistently exceed safe levels (typically above 80°C for most CPUs), it may indicate that cooling solutions need improvement.
3. Update Drivers and Software:
Regularly check for updates for your operating system and drivers.
Use Windows Update for OS updates and check the manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers for your hardware.
4. Scan for Malware:
Perform regular system scans using antivirus software to detect and remove any malware.
Schedule scans to run periodically and consider enabling real-time protection features.
5. Control Background Processes:
Identify and manage resource-heavy applications using Task Manager.
Consider closing unnecessary applications that may be causing excessive CPU load.
6. Consider Manual Overclocking:
If you are comfortable with overclocking, consider doing it manually.
This approach allows you to set specific parameters for clock speed, voltage, and other factors, enabling better control over CPU performance.
7. Test Stability:
If you decide to overclock your CPU manually, always test for stability using software like Prime95 or AIDA64.
These tools can stress-test your CPU to ensure it operates correctly at the desired clock speeds without crashing or overheating.
FAQ’s
1. What causes my CPU to overclock itself?
Automatic overclocking features in CPUs, background processes, or certain BIOS settings can trigger self-overclocking.
2. How can I check if my CPU is overclocking?
You can monitor your CPU’s clock speed and temperature using tools like Task Manager, HWMonitor, or Core Temp.
3. Is self-overclocking harmful to my CPU?
While it can improve performance, self-overclocking may lead to overheating and instability if cooling solutions are inadequate.
4. How can I stop my CPU from overclocking itself?
You can disable automatic overclocking features in your BIOS/UEFI settings and ensure adequate cooling to maintain stable performance.
5. What should I do if my CPU is overheating?
Ensure your cooling system is sufficient, apply new thermal paste if necessary, and consider upgrading to a more effective cooling solution.
Conclusion:
Experiencing self-overclocking behavior from your CPU can be perplexing, but understanding the underlying causes can help you manage and control it effectively. By checking BIOS settings, monitoring temperatures, and keeping software up to date, you can optimize your CPU’s performance while ensuring system stability.